uml-sp
Object-oriented simulation language UML2 SP
This project is maintained by vgurianov
Koch snowflake
Terms view on Wikipedia.
Introduction
Mathematical abstractions exist in conceptual reality (K.Popper, three worlds). The abstractions also can be simulated. Simulation model of mathematical abstraction build as simulation model of physical object. Simulation of mathematical abstraction has many general with constructive mathematics and used similar notions. Also, for simulation of mathematical objects are useful notions and ideas non-standard analysis, first of all notion of infinitesimal element. We shall discuss mathematical objects such as geometric fractals because main principle SSP methodology is decomposition principle which set approximate fractal structure of models. We shall considered object model of the Koch snowflake. The model proposed in work [1], also see [2].
Problem domain
A procedure of construction of the the Koch snowflake includes the following steps:
- choose initiator and generator (see Fig.1);
- apply generator (see Fig.1);
- change the scale of the generator to 1/3
and replace previous two steps n times. The polygon tends to the Koch snowflake as n → ∞.
It’s necessary measure a value of fractal dimension.
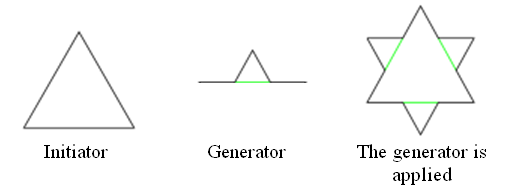
Figure 1. Applying generator
More info view on Wikipedia.
Analysis model
In UML2 SP, “space” notion is a container to components of system and denoted «Space» stereotype. But simulation model of mathematical object of “space” don’t isn’t «Space» class. Mathematical objects are objects of mental realty and simulate as objects of physical realty. «Exist» stereotype mean an operation to mathematical object. A conceptual model in UML2 SP is an analysis class diagram. This diagram considered as ontology. Model the fractal is depicted in Fig.2.
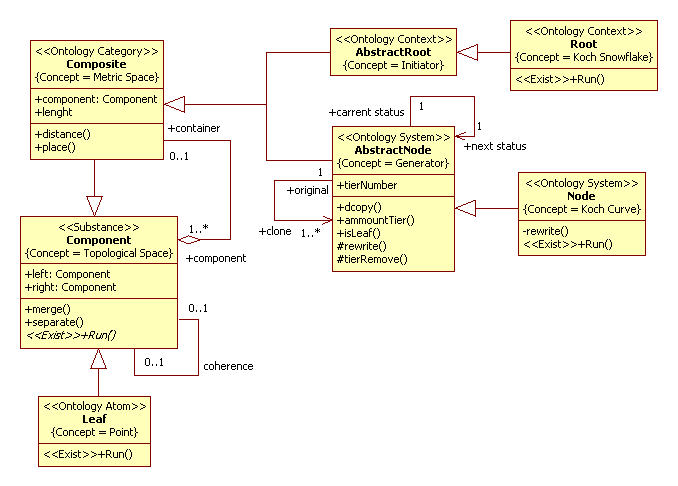
Figure 2. The class diagram
Description of a computational semantics
All objects of class have parallel threads.
Description of an application domain semantics
We shall give definition of concepts to the ontology.
Topological Space
The “Component” frame define “Topological Space ” concept. The frame has «left and right» slots. It is defined “coupling” notion.
Geometry Point
The “Leaf” frame define “Geometry Point” concept. Geometry Point
Metric space
The “Composite” frame define “Metric space” concept. A metric space is a set for which distances between all members of the set are defined. Those distances, taken together, are called a metric on the set. “length” slot define “metric” concept. “distance()” operation change a value of slot.
Generator
The “AbstractNode” frame define “Generator” concept. Generator is object which realise the following process:
- divide the line segment into three segments of equal length.
- draw an equilateral triangle that has the middle segment from step 1 as its base and points outward.
- remove the line segment that is the base of the triangle from step 2.
Method run this process is “revrite()” . “isLeaf” slot define “Is leaf” concept. It have “true” value if object lie bottom tier. The generator construct the Koch curve.
Initiator
The “AbstractRoot” frame define “Initiator” concept. The Initiator is initial object. If initiator is line then shall constructe Koch curves. The Koch snowflake can be constructed by starting with an equilateral triangle.
Non-standard elements
As mentioned above, for simulation of mathematical objects must use notions of non-standard analysis.
Object is non-standard element whenever can be executed rewrite operation.
For action to non-standard element, must remember this.
If bottom tier consist instance of Lief class then object is a approximate fractal.
If bottom tier consist instance of Node class then object is a fractal. It is potencial infinity object.
Now we represent simple example of non-standard element.
Infinitely large linked list is a list such that has rewrite operation. Let List be class of linked list, let Item be class of list item.
For List, defined next rewrite operation:
void leftRewrite() {
Item *ni = new Item;
ni->left = NULL;
ni->reght = head;
head = ni;
} ,
where head variable is head of linked list.
We can be define insertItem() or deleteItem() or other operation unless it do not conflict to rewrite operation.
The leftRewrite() operation extend List class of finite linked list (a program class is a set in mathematics),
added non-standard element. In considered case, it’s posible. Infinitely large linked list is a non-standard element. Also, first item of list is a non-standard element but item of list tail isn’t a non-standard element.
If List class has “divide” operation then Item class define infinitesimal elements.
Verification
We denote the box-counting dimension by d. Let e be a length of covering,
let n be an amount of elements of covering. First two a step can calculate to hand.
In the first step, p = 1, e = 1/3, n = 3x4 = 12, d =lnN(e)/ln(1/e) = 2.48490665/1.098612289 = 2.261859507.
In the second step, p = 2, e = (1/3)/3 = 1/9, n = 4x4x3 = 48, d = 3.871201011/ 2.197224577= 1.761859507.
In this way,
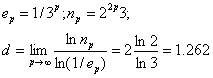
i.e., accurate value d is 1.262
The result of measurement to simulation model is shown on Fig. 3, where Dt is accurate value of box-counting dimension, eps is e.
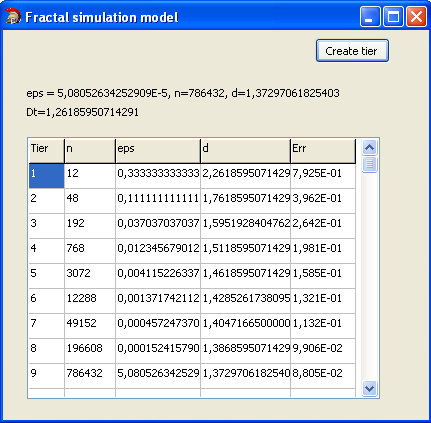
Figure 3. Results of measurement to simulation model
As we see, the measurement value of box-counting dimension converges to accurate value.
The simulation model in C++ code:
ClassesOfFractalProject.h, ClassesOfFractalProject.cpp
Conclusion
In this section considered object model of the Koch snowflake. This model can use to construct other fractals such as the Cantor ternary set and more complex.
In addition, other examples of simulation model of mathematical objects see [3].
References
- Gurianov V.I. Object Modeling of Fractal Structures // Mathematical Models and Their Applications: Sat. sci. tr. Issue. 13. - Cheboksary: Publishing house Chuvash. University, 2011.- P. 148-159
- V.I. Gurianov, Simulation with UML SP. Cheboksary: SPbSEU, branch in Cheboksary, 2014. - 136 p.(In Russian)
- Shamin R.V. Modern numerical methods in object-oriented presentation in C #, - 2011. (In Russian)