uml-sp
Object-oriented simulation language UML2 SP
This project is maintained by vgurianov
UML2 SP conception
The UML2 SP is result of development of conception represent in work (Richter et al. 2000) but include a series of significantly new ideas. This is the following three propositions: communicative paradigm, double semantics, and semiotic approach.
Communicative paradigm. Any object of reality is a communication process consist an elementary acts of communication. It is an abstraction like a matematical abstration. We regard the history of object-oriented approach as a history of a discovery of discrete world.
Double semantics. Any element of UML2 SP has a dauble semantics: problem domain semantics and computinal semantics. An object is a communication process and a computinal simulation is communication process. In simulation, a communicative process is general abstration, it is an invariant.
In problem domain semantics, Analysis Class Diagram is an ontology of problem domain. In computinal semantics, Analysis Class Diagram is model of program.
Semiotic approach. The triangle of reference (a semantic triangle) is a triangle: Symbol—Meaning— Thing (a referent). The triangle we consider as a model of stereotype. It is abstract stereotype AbstractConceptualElement. The “referent” is a stereotype, the “meaning” is a tagged value of Concept, and “symbol” is a tagged value of ID. All stereotypes of UML2 SP are children AbstractConceptualElement stereotype. For example, the “author The Adventures of Tom Sawyer” situation is modeled as
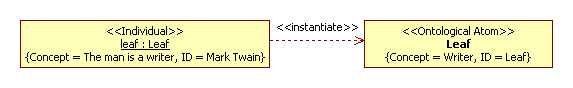
(but if Concept = Human for Leaf then Concept = The man is a human and ID = Samuel Clemens for leaf object; Mark Twain is the pseudonym Samuel Clemens).
Сlarify this picture:
- UML-element “Class” for object:
Concept = The man is a writer, i.e. object is an instance of class. Usually this tagged value hidden on diagram.
ID = Mark Twain, i.e. individual name of object. - UML-element “Class” for class:
Tagged value Concept is notion, meaning of term.
Tagged value ID is designation of notion. Conveniently designation of notion denotes as name of class then this tagged value can hide on diagram.
Attributes and operations also define concepts and as rule hidden on diagram but those elements locate in model.
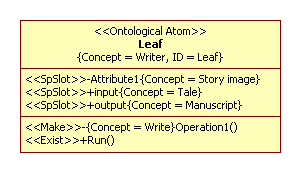
If object or class has SP-stereotype then it is considered as frame by Marvin Minsky. It much similar to description of ontology in Protégé. Not all classes are frames; most classes are defining of types of slots. Slots define semantics of these classes. A type is a set of value and authorized operations.